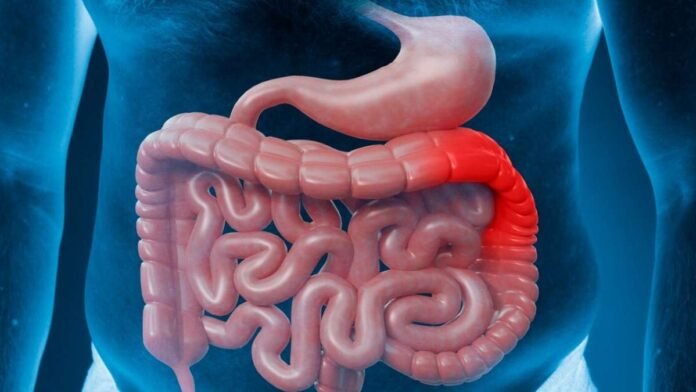
Colon cancer begins in the colon or rectum. Colon and rectum digest food and remove waste. The WHO estimates that it accounts for 10% of all cancer cases and is the third most common malignancy and second major cause of cancer mortality.
Benign polyps can turn cancerous. These polyps can metastasize and infect nearby tissues if left untreated.
Emerging colon cancer tendencies in youth are worrisome Most colon cancer cases are in elderly persons, however younger adults are being diagnosed.
Dr. Manish Sharma, Senior Medical Oncologist at Action Cancer Hospital, New Delhi and Cancer Care Clinic Faridabad, said, “While colon cancer has hereditary predispositions, external factors are likely to blame for the significant rise in incidents Smoking, inflammatory bowel disease, poor diet, obesity, and alcohol abuse increase colon cancer risk.
The rise in young colon cancer patients underscores the need to enhance awareness of its signs. Rectal bleeding, bowel irregularities, abdominal pain, and unexplained weight loss may be missed in younger persons with colon cancer. Early detection and treatment require proactive screening and expertise.
Dr. Manish Sharma suggested a few lifestyle changes to reduce colon cancer risk.
Reduce red meat, especially processed or charred, to prevent colon cancer. Cooking with high fat and protein may impact cancer-causing chemical production. Grilling and smoking red meat may be related. High-temperature cooking can release cancer-causing chemicals. Try plant protein and fish or chicken for lean protein.
Eat less sugar. Sugary drinks raise breast, colon, and other cancer risks. Sugar raises insulin resistance, obesity, and cancer risk. Sugar metabolism may potentially fuel cancer. Dr. Sharma underlines the conflicting cancer risk evidence from artificial sweeteners. Like sugar, he advises moderation with artificial sweeteners.
For constipation, blood sugar, heart, and intestinal health, eat lots of fibre. Additionally, it lowers colon cancer risk. In 2018, dietary fiber was found to prevent colon cancer in numerous ways. This includes optimizing bowel movements and lowering digestion-related carcinogens.
The CDC says alcohol raises mouth, throat, colon, rectum, liver, and breast cancer risk. The body breaks down alcohol into acetaldehyde, which destroys cell DNA and may stimulate uncontrolled cell development, causing malignant tumors. Even moderate drinking raises colon cancer risk. You would rather quit drinking.