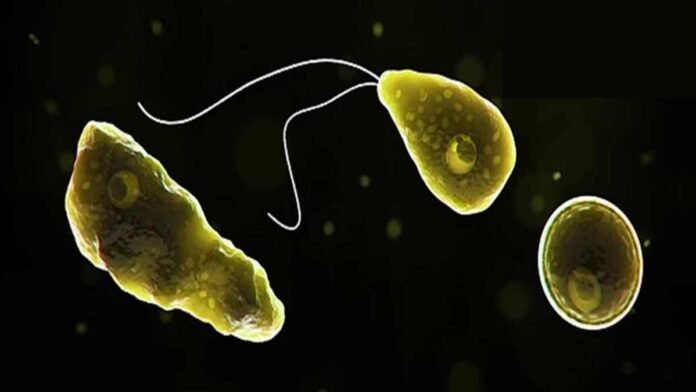
Naegleria fowleri, also known as the “brain-eating amoeba,” was first detected in South Korea on Monday, according to The Korea Times. According to the authorities, a 50-year-old Korean national who had just returned from Thailand passed away 10 days after exhibiting symptoms of the extremely rare but deadly infection.
The man spent four months in Thailand before arriving in South Korea on December 10, according to the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (KDCA). The report stated that he was taken to the emergency room the following day after developing headaches, vomiting, neck stiffness, and slurred speech.
On December 21, he passed away. Numerous tests were performed by health authorities to identify the precise cause of his demise, which was later determined to be an infection brought on by Naegleria fowleri.
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention describe Naegleria as an amoeba, a single-celled organism, and state that only one species of it, Naegleria fowleri, can infect people (CDC). It was first found in Australia in 1965, and warm freshwater areas like hot springs, rivers, and lakes are where it is most frequently found today.
How does it infect humans?
The human body is infected by the amoeba through the nose, where it then ascends to the brain. When someone swims, dives, or even just dips their head into a freshwater body, this frequently occurs. It was discovered that in some instances, people contracted an infection after cleaning their nostrils with contaminated water. There is no proof that Naegleria fowleri spreads through aerosol or water vapor, according to scientists.
The CDC states that once Naegleria fowleri enters the brain, it damages brain tissue and results in primary amebic meningoencephalitis (PAM), a potentially fatal infection.
What are the symptoms of PAM?
According to the CDC, PAM symptoms begin to manifest one to 12 days after infection. In the early stages, they may resemble the headache, nausea, and fever symptoms of meningitis. Later symptoms may include a stiff neck, seizures, hallucinations, and even coma. The US public health organization also noted that the infection spreads quickly and typically results in death within five days.
Out of 154 people who were known to have PAM in the United States between 1962 and 2021, only four managed to survive, according to the CDC.
What is the treatment for the infection?
There are currently no known effective treatments for Naegleria fowleri infection because it is uncommon and spreads rapidly. A combination of medications, including amphotericin B, azithromycin, fluconazole, rifampin, miltefosine, and dexamethasone, is currently being used by doctors to treat it.
Can climate change increase the spread of the infection?
The Naegleria fowleri amoeba primarily thrives in warm freshwater bodies, so the CDC claims that as global temperatures rise, so will the likelihood of contracting the infection. The organism thrives in high temperatures up to 46°C and can occasionally endure temperatures even higher.
Numerous recent studies have discovered that too much atmospheric carbon dioxide has contributed to an increase in lake and river temperatures. For the amoeba to grow, these circumstances offer a better environment. According to the CDC website, heat waves, when air and water temperatures may be higher than usual, may also promote the amoeba’s growth. Infections in the US were initially primarily reported in southern states, but in more recent years, they have also been seen in northern states, it also says.
For latest Bollywood Update Follow us on Instagram & Watch on Youtube